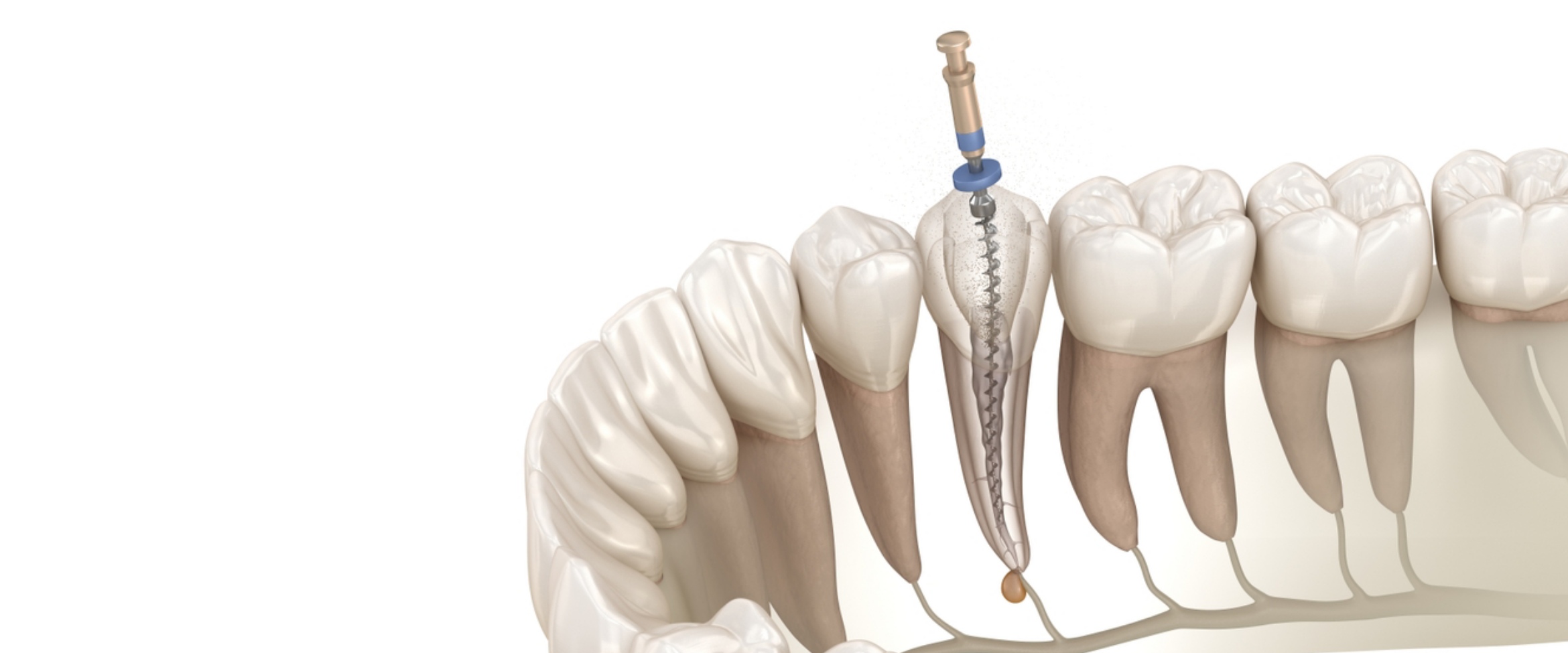
The root of the tooth is the lower part of the tooth that is attached to the jawbone. The root of the tooth is made of a hard tissue called dentin, and in the center of the root of the tooth is a canal that contains nerves and blood vessels.
Given the importance of the root of the tooth in maintaining the health of the tooth, this part of the tooth connects to the jawbone and helps it stay in place. Also, the nerves and blood vessels in the root of the tooth help the tooth receive nutrients and stay healthy.
In this article, we will examine the structure and function of the tooth root. We will also mention some diseases related to the root of the tooth and how to treat them.
Location of the tooth root
The root of the tooth is one of the vital parts of each tooth and is located inside the jaw. The number of roots in each tooth is between one and three, and their number varies depending on the location of the tooth. When your tooth hurts and its root is inflamed, it is necessary to clean all the root canals from infection. Otherwise, the infection will spread quickly throughout the tooth and you will have to have it extracted.
Dental canal
The pulp is the cavity in the center of each tooth that is made up of soft tissues such as nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissue. This cavity is covered by a covering of enamel and dentin. Blood vessels are important for supplying nutrients to the pulp and sensory nerves for transmitting nerve messages to the brain.
In root canal treatment, pain is relieved by causing irreversible damage to the pulp. The anatomy of the root canal includes the pulp chamber and the root canals. The secondary root canals are mostly located at the end of the root and may be present in any part of the root. The number of root canals depends on the number of roots and the type of tooth and can vary. Abnormal shape of the root canal and the presence of multiple canals for one root are important factors in the failure of root canal treatment.
Root Canal and Vascular Nerves
The canal of the tooth contains various nerve tissues and blood vessels, and when a tooth hurts, these nerves are compressed and damaged. Most treatments are performed on the canal of the tooth, and if not treated immediately, decay and the accumulation of germs and bacteria in the root canal can lead to severe swelling and infection at the end of the tooth root.
Types of Tooth Roots
Each human tooth has at least one root and one root canal. The root of a tooth can have one, two, or three canals. The roots of the tooth may be separate or connected to each other. Accurately diagnosing the type of tooth root helps dentists to properly treat the root canal.
The number of root canals of teeth is as follows:
-Upper incisors: one canal
-Upper canines: one canal
-Upper first premolars: two canals
-Upper second premolars: one or two canals
-Upper molars: three or more canals
-Lower incisors: one canal
-Lower canines: one canal
-Lower premolars: one canal
-Lower molars: two or more canals
Tooth roots
Teeth are divided into two main categories:
-Anterior (front) and posterior (back) teeth. Each of these groups has a certain number of roots.
-Anterior teeth include the central incisors (upper and lower), lateral incisors, and canines (canines). In these teeth, each has only one root.
Posterior teeth include the upper and lower premolars and the upper and lower molars. Within this group, the number of roots varies.
-Upper premolars have one to two roots.
-Upper second premolars have one to two roots.
-Lower premolars have only one root.
-Upper first, second, and third molars each have three roots.
-Lower first, second, and third molars each have two roots.
It should be considered as a general assumption that every human tooth has at least one root and one root canal. However, in some breeds and in some teeth, the number of canals or roots may be less or more than normal. In general, the number of canals and roots may vary in certain cases. Therefore, root canal treatment may vary from person to person and from tooth to tooth and requires careful attention and examination by the dentist.
How is the type of tooth root diagnosed?
The type of tooth root and root canal can be diagnosed in two ways: a dental examination and imaging with two-dimensional and three-dimensional radiographs.
Two-dimensional radiography:
This method is the most common method of dental imaging. In this method, a two-dimensional and flat image of the tooth is obtained that does not show the depth of the image. For better diagnosis, dentists obtain several radiographs of the tooth, changing the angle of the X-ray to a positive and negative angle of 20 degrees.
Three-dimensional tomography:
The use of cone-shaped computed tomography in dentistry has become very common in the past decade. In this method, the type of tooth root is completely determined with a single imaging session.
Accurate diagnosis of the tooth root is very important because it helps dentists to perform root canal treatment and repair tooth decay well.
Steps to Root Canal Treatment by a Dentist
To diagnose and treat root canals and the root of the tooth, the dentist first uses an X-ray to take an image of the tooth to examine the shape of the root canals and identify any problems. At this stage, a sheet or rubber is placed over the tooth to prevent contamination and you can breathe normally.
Then, the dentist uses a local anesthetic to numb the area around the tooth. The number of canals in each tooth may be between 1 and 4. The dentist cleans, shapes, and disinfects all the canals. This process may take several visits, and at each visit, the tooth is strengthened with a special temporary filling material. A metal band may also be placed around the tooth for additional protection.
After treatment is complete, the root canal space is filled with a material called gutta-percha. A small abutment may also be placed inside the root canals to strengthen the tooth. If necessary and there is a large cavity, a crown is also placed on the tooth.
Root canal and root canal treatment may take longer than a regular filling, but is often performed in the same painless way.
Differences in canals
In some cases, a greater number of roots are observed in the tooth. Of course, it should be noted that this is a rare phenomenon. While the number of canals is greater than the usual number, it is very common.
Multiple and connected roots
Sometimes the roots of a tooth may connect to each other and fuse together. This occurrence of root connection and fusion is a bit unpredictable. Also, the difference in the number of root canals of the teeth is not rare and unusual.
The treatments that should be performed on these cases will be discussed below.
Examining the difference between canals and tooth roots
In the structure of the tooth, the root and canal are two main parts and have separate concepts. Sometimes, a mistake occurs and people think that the root and the canal are the same concept, while each of these elements has independent characteristics and functions. The most important differences between the canal and the root of the tooth are:
Tooth root:
The root is the lower part of the tooth that is connected to the jawbone. The roots are conical or cylindrical in shape and their main function is to connect the tooth to the jaw. It mainly consists of nervous tissue.
Tooth canal:
The canals enter the root of the tooth and are the space where the nerves, blood vessels and tendon tissue of the tooth are located. The function of the canals is to transport these elements to and from the root of the tooth.
Therefore, the root and the canal are two separate and independent concepts and have different functions in the structure and function of the tooth.
Difference between canal and tooth root
The tooth canal is a subset of the root of the tooth that is located inside it. These canals are the internal part of the root of the tooth and it is impossible to see them with the naked eye. Even if part of the tooth is decayed and emptied, you will still not be able to see the tooth canal.
Root Structure and Tooth Canal
A tooth canal is an independent part that is considered part of the tooth root. When a tooth is removed due to decay, it is not possible to treat and repair the canal and it is better to replace it with an implant or a dental bridge. In the structure of the tooth root, in addition to the canal, there are other components such as the pulp. These components include enamel, dentin, pulp, and canal.
Reasons for tooth root resorption
The main reasons for tooth root resorption can include tooth type, genetics, and hereditary factors. In addition, failure to observe oral hygiene and failure to brush your teeth on time and after each meal can also lead to tooth root resorption. Harmful bacteria in the mouth can develop and damage the teeth and ultimately the roots by accumulating and rotting food residue on the teeth.
Dental infections can also be another reason for tooth root resorption. Failure to repair teeth whose crowns have been lost and the root is left unused can also lead to a decrease in the strength of the tooth root and its resorption. Also, using a crown on teeth whose crowns have been lost can keep the tooth root alive and prevent it from resorption.
In cases where the tooth root has shortened to the point that a crown cannot be installed on it, a dental implant can be used as an option to replace teeth and prevent edentulism.
Another way to prevent and reduce tooth decay is to consume dairy products such as milk, yogurt, and cheese to provide calcium and strengthen bones, especially the roots of the teeth.
The reasons for tooth decay can be divided into two categories. The first category includes hereditary factors such as tooth type and genetics, which are uncontrollable. The other category includes acquired factors that can be prevented by maintaining oral hygiene, brushing teeth on time, and restoring teeth.
Therefore, root canal treatment can be performed by preventing acquired factors and maintaining oral hygiene, and in some cases, the need for root canal treatment may include the following:
Inflammation and infection:
If the root of the tooth has decayed and bacteria and infection are present there, root canal treatment is necessary. In this method, bacteria and decayed tissue are cleaned from the root of the tooth, and then the root of the tooth is filled and treated.
Damage from a failed restoration:
If a restoration that was done on a tooth has failed and has caused the root to decay, the tooth will need to be treated. In this case, the previous restoration is removed, the root is filled, and a new restoration is placed.
Fractured or cracked tooth root:
If the root of a tooth is broken or cracked, root canal treatment is necessary. This may involve filling the root canal, using screws and pins to stabilize the root, or even removing the decayed tooth and replacing it with a dental implant.
Root canal treatment is usually performed by a dentist. After root canal treatment, the tooth will usually undergo a filling to improve its strength and function. It is important to maintain good oral hygiene after root canal treatment, such as brushing your teeth regularly, flossing, and taking good care of your mouth, to prevent further damage.
Symptoms of tooth root decay
The symptoms of tooth root decay in patients may vary, and in some cases, the patient may not have any of these symptoms. In other cases, the patient may experience some of the following symptoms:
-The affected tooth root may be sensitive to stimuli such as heat and cold, sugary foods and drinks.
-The patient may experience constant pain or shooting pain in the affected area. This pain may be sharp and sudden or chronic and ongoing.
-When the patient is chewing food, the affected tooth root may hurt.
-Injury to the tooth root can lead to inflammation and swelling of the gums around the tooth. As a result, the gums may become red and swollen.
-The patient may experience a feeling of looseness in the affected area. This sensation can be a sign of damage to the tissues around the tooth root.
-Root decay may lead to fractures of the enamel (the surface layer of the tooth). This fracture may appear as tiny cracks or larger gaps in the enamel.
- A decayed tooth root may cause discoloration of the enamel. These changes can include black, brown, or white spots on the surface of the tooth.
- Due to damage to the root of the tooth, the gums may recede and pull, causing leakage and an abnormality in the protection of the gums against bacteria.
- Tooth decay can lead to infection and sores around the tooth. These symptoms can include swelling, redness, pain, and discharge.
It is important to know that each person may experience different symptoms and some of these symptoms may not occur in some patients. It is best to see a dentist. The dentist will make the correct diagnosis for you by evaluating and examining the condition of your teeth and oral function and, if necessary, determine the appropriate treatment plan.
why you shouldn’t immediately get a tooth extracted?
Sometimes, when we experience tooth pain, humans may decide to have a tooth extracted. But we must say that this decision is a complete mistake and may cost you more. The following are some of the disadvantages of tooth extraction:
Dental space left:
After a tooth is extracted, a gap is left in the teeth. This may cause crowding and a change in the alignment of the surrounding teeth.
Increased risk of decay in other teeth:
By extracting a tooth, the balance in the dental arch is disrupted and may lead to decay in other teeth.
Replacement of teeth and their movement:
After a tooth is extracted, the adjacent and opposing teeth can gradually shift, causing a change in the alignment and balance of the teeth.
Facing the high cost of dental implants and implants:
If there is a need for replacement after tooth extraction, the use of implants or dental implants may be expensive.
Therefore, our advice for you in similar situations is to visit a dental clinic. In most cases, the problem can be solved by performing a restorative treatment and root canal treatment.
The right time for root canal and root canal treatment
Root canal treatment is a suitable method for treating damaged or infected teeth. With this method, the tooth can be restored to a healthy state. Teeth may be damaged and infected for reasons such as decay, the need for frequent dental work, wear and fracture, gum disease, old fillings, or trauma.
When the dental pulp is damaged, bacteria enter the tooth and spread there. These bacteria can cause infection or abscess in the tooth. An abscess is a pus-filled lump that forms at the end of the tooth root.
With root canal therapy, the damaged pulp is removed, the space inside the tooth is cleaned and then filled. This procedure helps the tooth return to a healthy state and the root infection is resolved. As a result, the symptoms of pain and swelling are reduced and the tooth is protected.
In general, root canal therapy is an effective method for treating damaged or infected teeth and ensures the improvement and maintenance of dental health.
Treatment of root decay and receding gums
Periodontal therapy:
This treatment is recommended for patients who have problems due to periodontal diseases, such as gum abscesses and receding gums. In this procedure, cleaning and surgery of the tooth root are performed so that the gum tissue becomes transparent and connects to the tooth surface.
Gum graft surgery:
If the receding gums have reached a severe stage, gum graft surgery may be required. In this procedure, gum tissue from another area of the mouth or artificial tissue is used and added to the receding gum area to connect directly to the root surface of the tooth.
Tooth restoration:
If the tooth has root decay, the decayed part of the tooth will need to be removed and the area filled. This procedure may involve the use of various dental filling materials.
Antibiotic treatment:
If there is a gum infection and a tooth abscess, your doctor may prescribe oral or topical antibiotics to treat the infection.
Tooth extraction:
If the root decay has spread into the tooth (pulp) and the nerve of the tooth, a tooth extraction may be necessary. In this procedure, the damaged pulp is removed and the root canal is cleaned to relieve infection and pain.
Tooth extraction and replantation:
If the damage to the tooth root is so extensive that it cannot be treated and rebuilt, you may need to have the tooth extracted and a denture used. In this procedure, the natural tooth is removed and a denture is placed in its place.
The bottom line
The tooth root is a complex and important structure that plays an important role in maintaining tooth health. This part of the tooth connects to the jawbone and helps it stay in place. The nerves and blood vessels in the root of the tooth also help the tooth receive nutrients and stay healthy.
To keep the root of the tooth healthy, it is important to prevent tooth decay. Tooth decay can damage the root of the tooth and cause pain, swelling, and other problems. To prevent tooth decay, you should brush and floss regularly. You should also avoid sugary foods and drinks.
If you have tooth decay, it is important to see a dentist to detect and treat the decay early. Early treatment of tooth decay can prevent further damage to the root of the tooth.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can the root of the tooth be repaired?
In some cases, the root of the tooth can be repaired. For example, if tooth decay has damaged the root of the tooth, a root canal may be performed to save the tooth.
2. Can the root of a tooth be extracted?
In some cases, the root of a tooth may need to be extracted. For example, if a tooth abscess is not treated, the root of a tooth may need to be extracted.
3. Can the root of a tooth grow back?
No, the root of a tooth cannot grow back. The root of a tooth is formed during fetal life and then stops growing.
4. Can the root of a tooth become infected?
Yes, the root of a tooth can become infected. A root infection is a serious condition that can cause pain, swelling, and other problems.
5. Can the root of a tooth discolor a tooth?
Yes, the root of a tooth can discolor a tooth. If the root of a tooth is damaged, the tooth may become discolored and dark.